Hepatits
Treatment of hepatitis B infection depends on how active the virus is and whether you are at risk for liver damage such as cirrhosis.
Treatment of short-term (acute) hepatitis B
- Have been recently infected with the virus.
- Have the symptoms of an acute infection.
- Have chronic infection.
If you have not gotten a hepatitis B vaccine and think you may have been exposed to the virus, you should get a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) and the first of three shots of the hepatitis B vaccine(What is a PDF document?). It is important to receive this treatment within 7 days after a needle stick and within 2 weeks after sexual contact that may have exposed you to the virus. The sooner you receive treatment after exposure, the better the treatment works.
If you have the symptoms of acute infection, treatment with antiviral medicine usually isn't needed. Home treatment-such as eating well, drinking plenty of fluids, and avoiding alcohol and drugs- usually will relieve your symptoms.
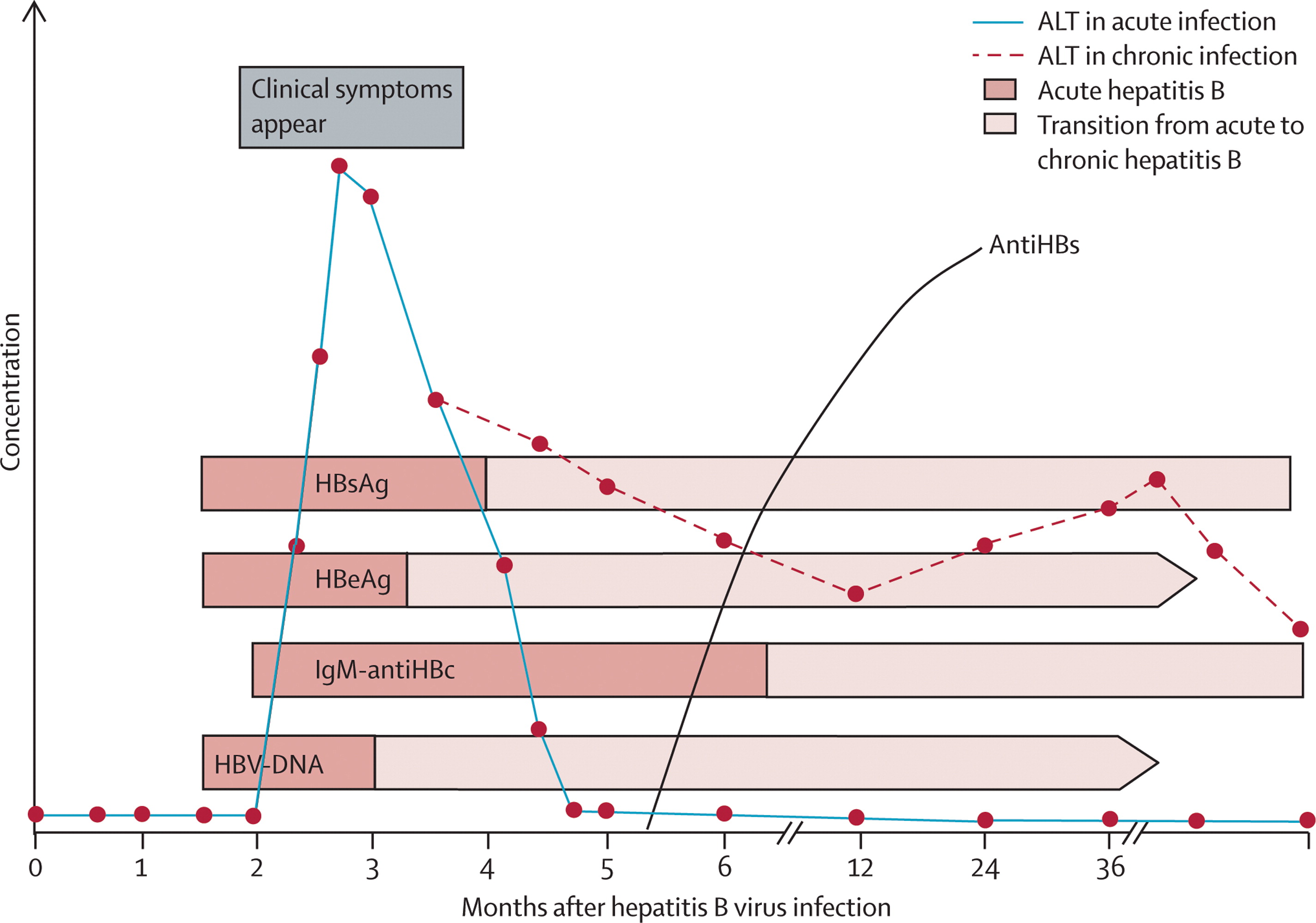
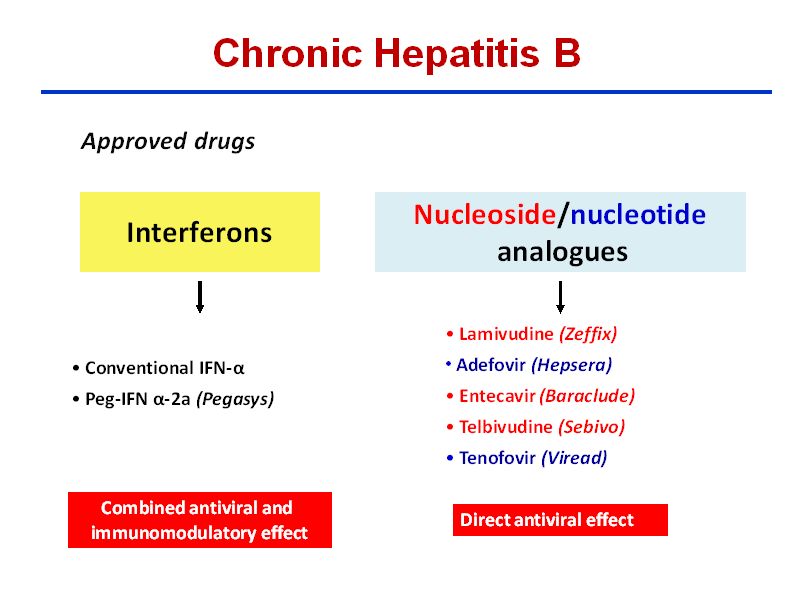
Treatment of long-term (chronic) hepatitis B
- Have been recently infected with the virus.
- Have the symptoms of an acute infection.
- Have chronic infection.
If you have not gotten a hepatitis B vaccine and think you may have been exposed to the virus, you should get a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) and the first of three shots of the hepatitis B vaccine(What is a PDF document?). It is important to receive this treatment within 7 days after a needle stick and within 2 weeks after sexual contact that may have exposed you to the virus. The sooner you receive treatment after exposure, the better the treatment works.
If you have the symptoms of acute infection, treatment with antiviral medicine usually isn't needed. Home treatment-such as eating well, drinking plenty of fluids, and avoiding alcohol and drugs- usually will relieve your symptoms.

