Special Test
TTG-1GA
What Is a Tissue Transglutaminase IgA (tTG-IgA) Test?
A tissue transglutaminase IgA (tTg-IgA) test is used to help doctors diagnose celiac disease. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune systemmistakenly thinks that gluten — a protein in wheat, barley, rye, and oats — is a foreign invader. The immune system makes antibodies that attack an enzyme in the intestines called tissue transglutaminase (tTG).
Why Are tTG-IgA Tests Done?
A tTG-IgA test may be done if a child has symptoms of celiac disease, such as poor growth, belly pain, constipation, vomiting, diarrhea, or rashes.
A tTg-IgA test also might be done if a child has a condition that makes celiac disease more likely (such as type 1 diabetes), thyroid disease, or a family member with celiac disease.
How Should We Prepare for a tTG-IgA Test?
For the test to be accurate, your child should be on a gluten-containing diet until the test is done.
Your child should be able to eat and drink normally unless also getting other tests that require fasting beforehand. Tell your doctor about any medicines your child takes because some drugs might affect the test results.
Wearing a T-shirt or short-sleeved shirt for the test can make things easier for your child, and you also can bring along a toy or book as a distraction.
How Is a tTG-IgA Test Done?
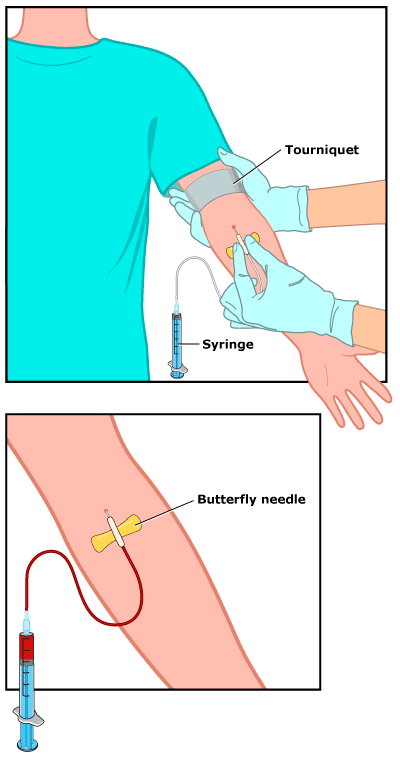
Most blood tests take a small amount of blood from a vein. To do that, a health professional will:
- • clean the skin
- • put an elastic band (tourniquet) above the area to get the veins to swell with blood
- • insert a needle into a vein (usually in the arm inside of the elbow or on the back of the hand)
- • pull the blood sample into a vial or syringe
- • take off the elastic band and remove the needle from the vein
IgE Test
What Is an Immunoglobulin E Test?
An immunoglobulin E (IgE) test measures the level of IgE, a type of antibody. Antibodies are made by the immune system to protect the body from bacteria, viruses, and allergens. IgE antibodies are normally found in small amounts in the blood, but higher amounts can be a sign that the body overreacts to allergens. This can lead to an allergic reaction.
IgE levels can also be high when the body is fighting off an infection from a parasite or with some immune system conditions.
Why Are IgE Tests Done?
An IgE test may be done if a child has signs of a possible allergy, immune system problem, or infection with a parasite.
How Should We Prepare for an IgE Test?
Your child should be able to eat and drink normally unless also getting other tests that require fasting beforehand. Tell your doctor about any medicines your child takes because some drugs might affect the test results.
Wearing a T-shirt or short-sleeved shirt for the test can make things easier for your child, and you also can bring along a toy or book as a distraction.
How Is an IgE Test Done?
Most blood tests take a small amount of blood from a vein. To do that, a health professional will:
- • clean the skin
- • put an elastic band (tourniquet) above the area to get the veins to swell with blood
- • insert a needle into a vein (usually in the arm inside of the elbow or on the back of the hand)
- • pull the blood sample into a vial or syringe
- • take off the elastic band and remove the needle from the vein
In babies, blood draws are sometimes done as a "heel stick collection." After cleaning the area, the health professional will prick your baby's heel with a tiny needle (or lancet) to collect a small sample of blood.
Collecting a sample of blood is only temporarily uncomfortable and can feel like a quick pinprick.


HLA B27 Test
What is this test?
This test looks for HLA-B27, which are proteins called antigens. These are found on the surface of white blood cells that are fighting infection. If you have HLA-B27, you may have an autoimmune disease. An autoimmune disease is when your immune system attacks your own cells. The most common autoimmune disorders connected with HLA-B27 antigens are:
• Ankylosing spondylitis, a form of arthritis that affects the spine
• Juvenile arthritis, which occurs in children
• Reactive arthritis, a type of arthritis in the joints
Your HLA antigens are unique to you. They are determined by your genes. Because of that, this blood test is also useful as a paternity test.
Why do I need this test?
You may need this test if your healthcare provider thinks that you have ankylosing spondylitis. This can cause pain and stiffness in your back, neck, or chest. This is more common if you are a man and have symptoms in your early 30s.
You also may need this test if you are having an organ or tissue transplant. For example, this may be a donor kidney or bone marrow. Your donor's HLA antigens must match yours for the transplant to have a chance to be successful.
Or a man may have this test to determine if he is the father of a child.
What other tests might I have along with this test?
If your HLA-B27 antigen test is positive, you may need other tests to help confirm a diagnosis of an autoimmune disease. You may have tests such as:
• Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) which may mean you have inflammation
• C-reactive protein, which also can look for inflammation
• Joint X-rays or MRI
• Urine test
What do my test results mean?
Test results may vary depending on your age, gender, health history, the method used for the test, and other things. Your test results may not mean you have a problem. Ask your healthcare provider what your test results mean for you.
A negative result mean you don't have HLA-B27 in your blood. A positive result means HLA-B27 was found in your blood. You may have a higher-than-average risk of certain autoimmune diseases, such as ankylosing spondylitis and reactive arthritis. If you are white, you are more likely to test positive for the HLA-B27 antigens.
If you need an organ or tissue transplant and your HLA antigens are not compatible with those of your donor, your body could reject the transplant.
In a paternity case, if the child or father has an unusual HLA genotype, paternity could be clear. If it's a common HLA genotype, the child could have many potential fathers.
How is this test done?
The test is done with a blood sample. A needle is used to draw blood from a vein in your arm or hand.

